Extremely Randomized (Extra) Survival Trees model
The Extra Survival Trees model is an extension of the Extremely Randomized trees model, introduced by Geurts et al in 2005, that can take into account censoring.
Instance
To create an instance, use pysurvival.models.survival_forest.ExtraSurvivalTreesModel.
Attributes
max_features: str or int -- The number of features randomly chosen at each split.num_trees: int -- number of trees contained in the foresttimes: array-like -- representation of the time axis for the modeltime_buckets: array-like -- representation of the time axis of the model using time bins, which are represented byvariable_importance: dict -- importance of each feature (the higher, the more important the feature is). The importance is the difference between the perturbed and unperturbed error rate for each feature.
Methods
__init__ - Initialize the estimator
ExtraSurvivalTreesModel(num_trees = 10)
Parameters:
num_trees: int (default=10) -- number of trees that will be built in the forest.
fit - Fit the estimator based on the given parameters
fit(X, T, E, max_features = 'sqrt', max_depth = 5,
min_node_size = 10, num_random_splits = 100, num_threads = -1,
weights = None, sample_size_pct = 0.63,
importance_mode = 'normalized_permutation', seed = None,
save_memory=False )
Parameters:
-
X: array-like -- input samples; where the rows correspond to an individual sample and the columns represent the features (shape=[n_samples, n_features]). -
T: array-like -- target values describing the time when the event of interest or censoring occurred. -
E: array-like -- values that indicate if the event of interest occurred i.e.: E[i]=1 corresponds to an event, and E[i] = 0 means censoring, for all i. -
max_features: int, float or string (default="sqrt") -- number of features to consider when looking for the best split:- If int, then consider the given value at each split.
- If float, then
max_featuresis a fraction andint(max_features * n_features)features are considered at each split. - If "sqrt", then
max_features=sqrt(n_features) - If "log2", then
max_features=log2(n_features). - If "all", then
max_features=n_features.
-
min_node_size: int (default=10) -- minimum number of samples required to be at a leaf node -
num_random_splits: int (default=100) -- number of random splits to consider for each candidate splitting variable. -
num_threads: int (default= -1) -- number of jobs to run in parallel during training. If -1, then the number of jobs is set to the total number of available cores. -
weights: array-like (default = None) -- weights for sampling of training observations. Observations with larger weights will be selected with higher probability in the bootstrap. The sum of the weights needs to be 1. -
sample_size_pct: double (default = 0.63) -- percentage of original samples used in each tree building -
importance_mode: str (default='impurity_corrected') -- variable importance mode. Here are the available options:impurityorimpurity_corrected: it's the unbiased heterogeneity reduction developed by Sandri & Zuccolotto (2008)permutationit's unnormalized as recommended by Nicodemus et al.normalized_permutationit's normalized version of the permutation importance computations by Breiman et al.
-
seed: int (default=None) -- seed used by the random number generator. If None, the current timestamp converted in UNIX is used. -
save_memory: bool (default=False) -- Use memory saving splitting mode. This will slow down the model training. So, only set toTrueif you encounter memory problems.
Returns:
self: object
predict_hazard - Predicts the hazard function
predict_hazard(x, t = None)
Parameters:
-
x: array-like -- input samples; where the rows correspond to an individual sample and the columns represent the features (shape=[n_samples, n_features]). -
t: double (default=None) -- time at which the prediction should be performed. If None, then return the function for all available t.
Returns:
hazard: numpy.ndarray -- array-like representing the prediction of the hazard function
predict_survival - Predicts the survival function
predict_survival(x, t = None)
Parameters:
-
x: array-like -- input samples; where the rows correspond to an individual sample and the columns represent the features (shape=[n_samples, n_features]). -
t: double (default=None) -- time at which the prediction should be performed. If None, then return the function for all available t.
Returns:
survival: numpy.ndarray -- array-like representing the prediction of the survival function
predict_risk - Predicts the risk score
predict_risk(x)
Parameters:
x: array-like -- input samples; where the rows correspond to an individual sample and the columns represent the features (shape=[n_samples, n_features]).
Returns:
risk_score: numpy.ndarray -- array-like representing the prediction of the risk score
Example
Let's now take a look at how to use the Extra Survival Trees (XST) model on a simulation dataset generated from a parametric model.
#### 1 - Importing packages import numpy as np import pandas as pd from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from pysurvival.models.simulations import SimulationModel from pysurvival.models.survival_forest import ExtraSurvivalTreesModel from pysurvival.utils.metrics import concordance_index from pysurvival.utils.display import integrated_brier_score %pylab inline #### 2 - Generating the dataset from a Exponential parametric model # Initializing the simulation model sim = SimulationModel( survival_distribution = 'exponential', risk_type = 'linear', censored_parameter = 1, alpha = 3) # Generating N random samples N = 1000 dataset = sim.generate_data(num_samples = N, num_features=4) # Showing a few data-points dataset.head(2)
| x_1 | x_2 | x_3 | x_4 | time | event |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.061498 | 7.065547 | 0.004457 | 0.131379 | 15.412209 | 0. |
| 0.079149 | 6.732271 | 0.008654 | 0.090398 | 0.000700 | 1. |
PySurvival also displays the Base Survival function of the Simulation model:
from pysurvival.utils.display import display_baseline_simulations display_baseline_simulations(sim, figure_size=(20, 6))

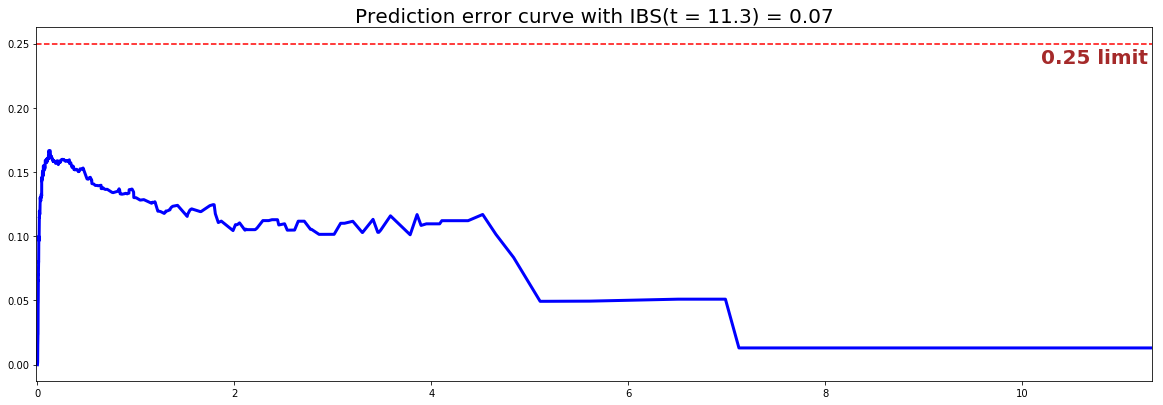
#### 3 - Creating the modeling dataset # Defining the features features = sim.features # Building training and testing sets # index_train, index_test = train_test_split( range(N), test_size = 0.2) data_train = dataset.loc[index_train].reset_index( drop = True ) data_test = dataset.loc[index_test].reset_index( drop = True ) # Creating the X, T and E input X_train, X_test = data_train[features], data_test[features] T_train, T_test = data_train['time'].values, data_test['time'].values E_train, E_test = data_train['event'].values, data_test['event'].values #### 4 - Creating an instance of the Conditional model and fitting the data. # Building the model xst = ExtraSurvivalTreesModel(num_trees=200) xst.fit(X_train, T_train, E_train, max_features="sqrt", max_depth=5, min_node_size=20, num_random_splits = 1000) #### 5 - Cross Validation / Model Performances c_index = concordance_index(xst, X_test, T_test, E_test) #0.81 print('C-index: {:.2f}'.format(c_index)) ibs = integrated_brier_score(xst, X_test, T_test, E_test, t_max=30, figure_size=(20, 6.5) ) print('IBS: {:.2f}'.format(ibs))
We can see that the c-index is well above 0.5 and that the Prediction error curve is below the 0.25 limit, thus the model yields great performances.
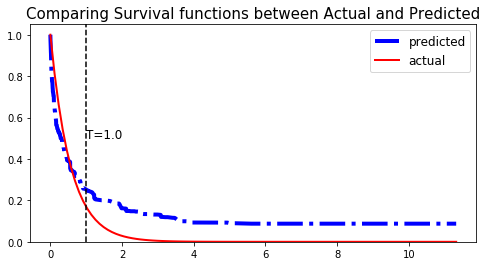
We can show this by randomly selecting datapoints and comparing the actual and predicted survival functions, computed by the simulation model and the XST respectively.
# Initializing the figure fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 4)) # Randomly extracting a data-point that experienced an event choices = np.argwhere((E_test==1.)&(T_test>=1)).flatten() k = np.random.choice( choices, 1)[0] # Saving the time of event t = T_test[k] # Computing the Survival function for all times t survival = xst.predict_survival(X_test.values[k, :]).flatten() actual = sim.predict_survival(X_test.values[k, :]).flatten() # Displaying the functions plt.plot(xst.times, survival, color = 'blue', label='predicted', lw=4, ls = '-.') plt.plot(sim.times, actual, color = 'red', label='actual', lw=2) # Actual time plt.axvline(x=t, color='black', ls ='--') ax.annotate('T={:.1f}'.format(t), xy=(t, 0.5), xytext=(t, 0.5), fontsize=12) # Show everything title = "Comparing Survival functions between Actual and Predicted" plt.legend(fontsize=12) plt.title(title, fontsize=15) plt.ylim(0, 1.05) plt.show()