How Add-ons Render
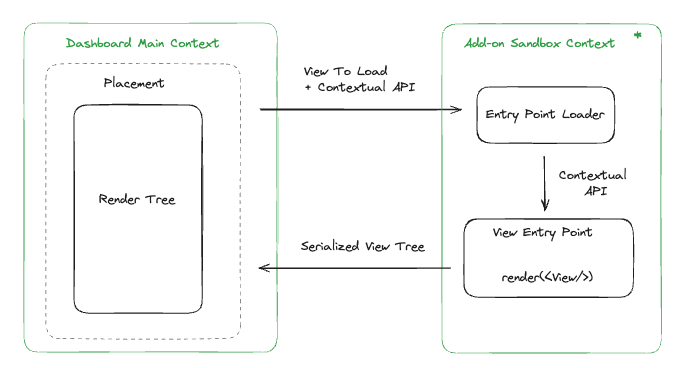
Execution and rendering of an Add-on takes place in separate contexts.
Execution of Add-on code takes place within a secondary JavaScript context hosted on the Dashboard. This context is isolated from the Dashboard as well as other Add-ons through native browser sandboxing.
Rendering of an Add-on takes place within the Dashboard’s main JavaScript context.
A developer defines the view they wish to render for a given placement within their manifest file. This is how the Dashboard knows what to load as the merchant views the placement. Placements are unique across the Dashboard and an Add-on may only define one view for a given placement.
{
"views":
{
"placement": "square.dashboard.customer.view",
"entry_point": "src/views/customer-view.tsx"
}
}
- When a merchant visits a page in the Dashboard there are placements which may render Add-ons. If an Add-on defines a view for the placement the views entry point is extracted and downloaded into the sandbox environment.
- Each placement has a unique API it supports providing contextual data to the Add-on. This API is provided to the Add-on view at runtime.
- The Add-on view returns a React component from its entry point. The component is serialized and provided to the Dashboard for rendering into the placement DOM.